In today’s digital world, organizations are increasingly managing devices that are not regularly connected to their internal networks. Whether dealing with remote employees, mobile devices, or clients and endpoints operating outside of the traditional boundaries, IT Administrators need a solution that extends the management capabilities beyond the corporate firewall. The Cloud Management Gateway (CMG) provides exactly that: a simple way to manage Configuration Manager clients over the Internet (Cloud Service). In this guide, we will explore what a Cloud Management Gateway is, how it works, and why we should care about this highly effective feature.
What is Cloud Management Gateway (CMG)?
The Cloud Management Gateway (CMG) feature within Microsoft’s Configuration Manager (ConfigMgr) allows organizations to manage client devices over the Internet, eliminating the need for VPNs or a direct connection to the organization’s internal network. Once deployed in Microsoft Azure, it essentially extends your on-premises infrastructure into the cloud without exposing it to the Internet, enabling remote devices to receive updates, patches, and configurations securely and reliably.
Through CMG, IT administrators can manage Configuration Manager clients outside the internal network as long as they are connected to the internet, ensuring devices are compliant, secure, and up to date with minimal effort.
How Does a Cloud Management Gateway Work?
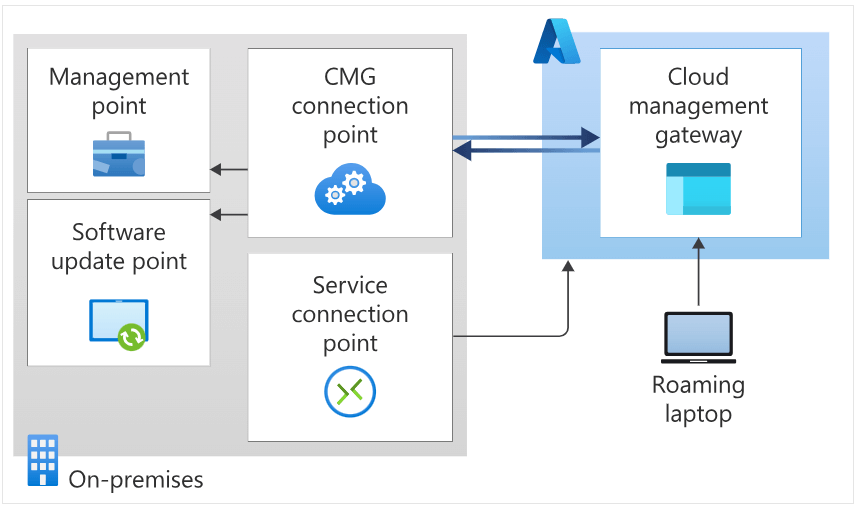
The CMG acts as a middleman, handling client requests and passing them on to the Management Point and Software Update Point (SUP). Clients communicate with the CMG service in Azure, which routes this communication through the CMG Connection Point. This serves as a bridge between the Azure service, the CMG, and your Configuration Manager infrastructure, ensuring seamless connectivity. From there, the CMG Connection Point forwards all requests to your Management Point and SUP.
All these components together help your Configuration Manager clients and roaming devices contact your Management Point and SUP.
You can visit Microsoft’s Data Flow CMG page for more in-depth information.
When to Use a Cloud Management Gateway
The need for a Cloud Management Gateway has increased dramatically with the rise of remote and hybrid work environments. Here are some scenarios where a CMG can be ideal:
If you have an increased number of remote employees, it is important to ensure those remote devices are managed and updated even when they are not connected to the internal network.
If you manage devices across multiple locations over the internet, using a CMG is more cost-effective than connecting office networks through a Wide Area Network (WAN).
If you want to minimize the reliance on VPNs for device management, CMG can increase efficiency while reducing time and cost.
If your organization has roaming devices, CMG can keep them secure and compliant by regularly patching them.
Why Should I Care?
Implementing a Cloud Management Gateway offers significant benefits to organizations managing a distributed workforce:
CMG enables organizations to manage roaming and hybrid devices as efficiently as their on-premises systems, ensuring consistent patching, security updates, and configuration compliance.
By keeping remote devices updated with patches (including third-party patches), CMG can help protect against vulnerabilities and cyberattacks, even when the devices are not connected to the on-premises infrastructure.
CMG does not require the clients to connect via VPN to communicate with the site system servers (Management Point or Software Update Point), which can be very costly.
As your organization grows, you can scale your management services easily with no additional on-premises infrastructure investment.
Cloud Management Gateway Setup
Setting up a Cloud Management Gateway can seem daunting, but the process can be broken down into manageable bite-size pieces. To start, Microsoft has a great CMG Set Up Checklist, but here is a basic outline to get started.
Azure subscription: CMG operates through Azure, so you must secure an Azure subscription and connect it to your Configuration Manager infrastructure.
CMG server authentication certificate: Because CMG uses HTTPS for secure client communication over the Internet, you can either use a certificate from a public, trusted certificate provider or a certificate issued by a Certificate Authority from your Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
Microsoft Entra ID: you can integrate the Configuration Manager site with your Microsoft Entra tenant by creating app registrations in Microsoft Entra ID. This allows the Configuration Manager site to authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID to deploy and monitor the CMG service.
Configure client authentication: because Configuration Manager clients communicate over the internet, you can use Microsoft Entra ID, PKI certificates, or token-based authentication from the site server for client authentication.
Set up the CMG: this includes configuring the primary site for client certificate authentication, adding the CMG Connection Point site system role, and configuring the Management Point and Software Update Point (SUP) for CMG traffic.
Configure Configuration Manager clients to use the CMG: There are two methods to install the Configuration Manager client on devices not connected to the internet: use a bulk registration token or run the ccmsetup.exe command. For the second option, the devices must be joined to a Microsoft Entra or hybrid Entra domain.
For more information on setting up a CMG in your environment, including a detailed walkthrough, check out our Patch My PC webinar. We explain the entire process step-by-step.
How to Use CMG for Third-Party Patching
Using a Cloud Management Gateway for third-party patching is a great way to increase both the security and the compliance of your IT infrastructure. By enabling remote third-party application updates, you can ensure that all Configuration Manager client devices, regardless of their physical location, remain secure and up to date. In addition to deploying third-party updates, you can also add a custom catalog from a third-party application patching vendor to Configuration Manager.
Leveraging Patch My PC with a CMG provides a powerful solution for third-party application and patch management, especially for remote or distributed environments.
The benefits of using Patch My PC with CMG are vast:
Patch My PC automates third-party application packaging, reducing the manual effort involved.
The Patch My PC catalog currently supports 2,000+ products.
Improve security by patching vulnerable third-party applications.
You can set it and forget it. Once the initial configuration is completed, all future updates will be packaged and published to Configuration Manager automatically.
Summary
The Cloud Management Gateway is a powerful solution for organizations managing an increasing number of remote and hybrid devices. CMG simplifies everything from seamless patching of both Windows and third-party applications to the secure, efficient management of off-network devices, making life easier for IT Administrators.
After reading this guide, you should now have a solid understanding of what a CMG is, how it works, when and why to use it, and the steps and resources to set it up. With the growing need for third-party application patching, CMG helps to keep remote devices secure and compliant. For a more automated approach to patch management, consider using Patch My PC.
