By using a script to deploy the Patch My PC (PMPC) certificate, you can either deploy the certificate as a:
In environments where a company configures an all-signed PowerShell policy or enforces script signature checking on the Win32 app in the Intune admin center, all scripts must be signed by a trusted publisher. Our script helps import the required certificate into the Trusted Publisher store to ensure that scripts signed by PMPC can be executed without issues.
To deploy our code signing certificate using a script, first download our scripts from:
https://github.com/PatchMyPCTeam/Community-Scripts/tree/main/Other/Code%20Signing
**Note**
You can find out more details about these scripts and what they do by reviewing the ReadMe.md file included with the scripts.
Certificates to Deploy
There are two distinct use cases in PMPC Cloud that require separate certificates:
- Intune Detection and Requirement Scripts
Used to sign Intune detection and requirement scripts for Win32 applications published through PMPC Cloud. - Patch My PC Helper Scripts
Used to sign required and recommended pre/post “helper” scripts for certain applications in the PMPC catalog. These helper scripts perform essential tasks such as stopping processes, uninstalling older software versions, or configuring application behavior during deployment to ensure successful app installation.
1. Deploy the Certificate use to sign Intune Detection and Requirement Scripts
To deploy our certificate using a script, follow Create a script policy and assign it using the following values.
“Platform scripts” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Add | Windows 10 and later |
“Basics” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | A descriptive name for the policy. E.g. “Patch My PC Cloud Trusted Publisher Certificate”` |
| Description | Enter an optional description for the policy |
“Script Settings” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Script location | Browse to and select Import-PMPCCloudTrustedPublisherCertificate.ps1 |
| Run this script using the logged on credentials | No |
| Enforce script signature check | No |
| Run script in 64 bit PowerShell Host | No |
“Scope tags” tab
Configure as required.
“Assignments” tab
Assign the configuration template to the desired Entra ID group(s).
“Review + add” tab
Double-check everything before clicking Add.
2. Deploy the Certificate use to sign Patch My PC Helper Scripts
To deploy our certificate using a script, follow the Create a script policy and assign it article using the following values.
“Platform scripts” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Add | Windows 10 and later |
“Basics” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | A descriptive name for the policy. E.g. “Patch My PC Apps Trusted Publisher Certificate”` |
| Description | Enter an optional description for the policy |
“Script Settings” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Script location | Browse to and select Import-PMPCAppsTrustedPublisherCertificate.ps1 |
| Run this script using the logged on credentials | No |
| Enforce script signature check | No |
| Run script in 64 bit PowerShell Host | No |
“Scope tags” tab
Configure as required.
“Assignments” tab
Assign the configuration template to the desired Entra ID group(s).
“Review + add” tab
Double-check everything before clicking Add.
Post Processing
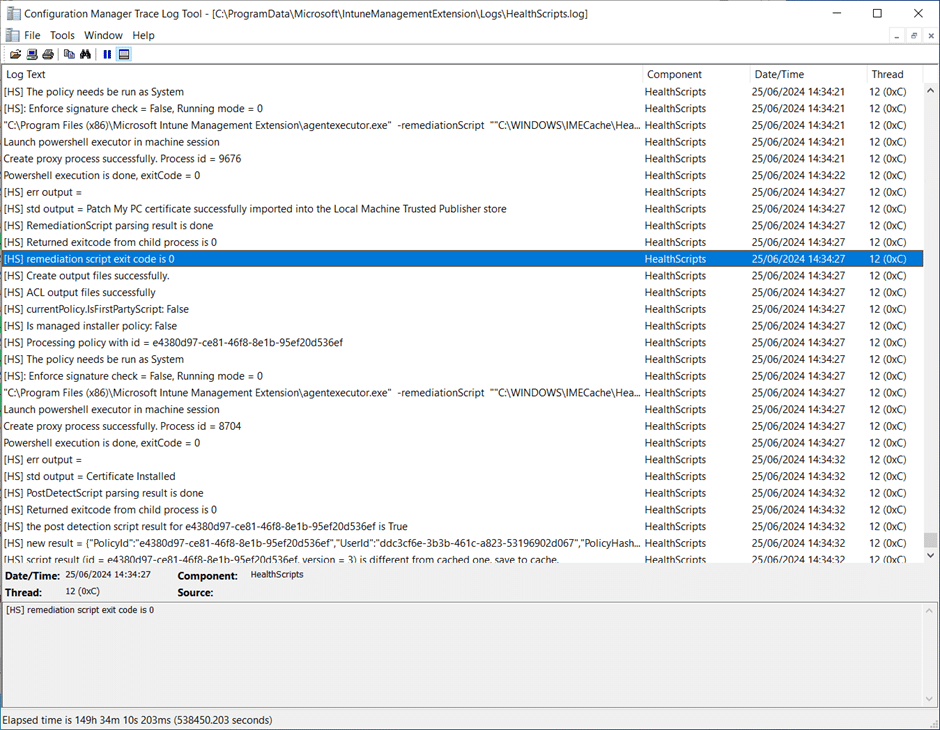
You can see the script being processed by the Intune Management Extension by looking in the IntuneManagementExtension.log located at:
%ProgramData%MicrosoftIntuneManagementExtensionLogs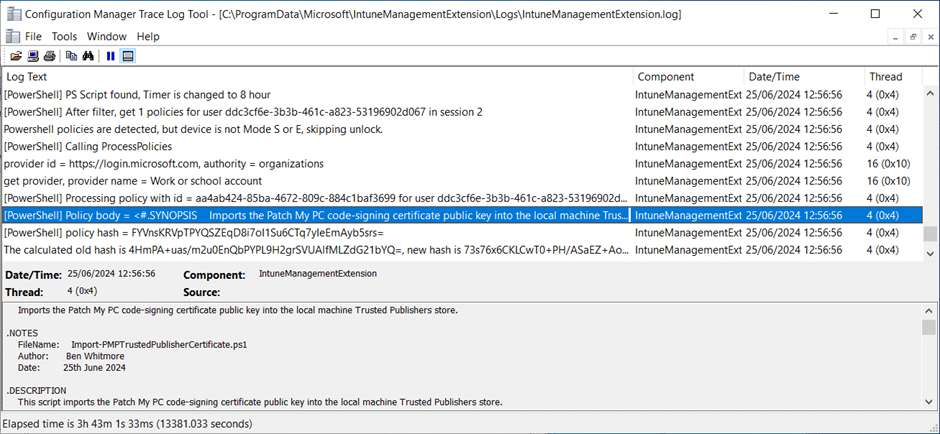
Using a proactive remediation
To deploy our certificate using a proactive remediation deployment, follow the Remediations article. The Remediation detection scripts can be found in the following repoistory on GitHub https://github.com/PatchMyPCTeam/Community-Scripts/tree/main/Other/Code%20Signing
1. Deploy the Certificate use to sign Intune Detection and Requirement Scripts
“Basics” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | A descriptive name for the policy. E.g. “Patch My PC Cloud Trusted Publisher Certificate”` |
| Description | Enter an optional description for the policy. |
| Publisher | Enter “Patch My PC” |
“Settings” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Detection script file | Browse to and select PMPCCloudTrustedPublisherCertificate_HealthScript_Detection.ps1 |
| Remediation script file | Browse to and select Import-PMPCCloudTrustedPublisherCertificate.ps1 |
| Run this script using the logged on credentials | No |
| Enforce script signature check | No |
| Run script in 64 bit PowerShell Host | No |
“Scope tags” tab
Configure as required.
“Assignments” tab
Assign the configuration template to the desired Entra ID group(s), then configure the frequency you want the Proactive Remediation to be executed on the targeted devices.
“Review + create” tab
Double-check everything before clicking Create.
2. Deploy the Certificate use to sign Patch My PC Helper Scripts
“Basics” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | A descriptive name for the policy. E.g. “Patch My PC Apps Trusted Publisher Certificate”` |
| Description | Enter an optional description for the policy. |
| Publisher | Enter “Patch My PC” |
“Settings” tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Detection script file | Browse to and select PMPCAppsTrustedPublisherCertificate_HealthScript_Detection.ps1 |
| Remediation script file | Browse to and select Import-PMPCAppsTrustedPublisherCertificate.ps1 |
| Run this script using the logged on credentials | No |
| Enforce script signature check | No |
| Run script in 64 bit PowerShell Host | No |
“Scope tags” tab
Configure as required.
“Assignments” tab
Assign the configuration template to the desired Entra ID group(s), then configure the frequency you want the Proactive Remediation to be executed on the targeted devices.
“Review + create” tab
Double-check everything before clicking Create.
Post Processing
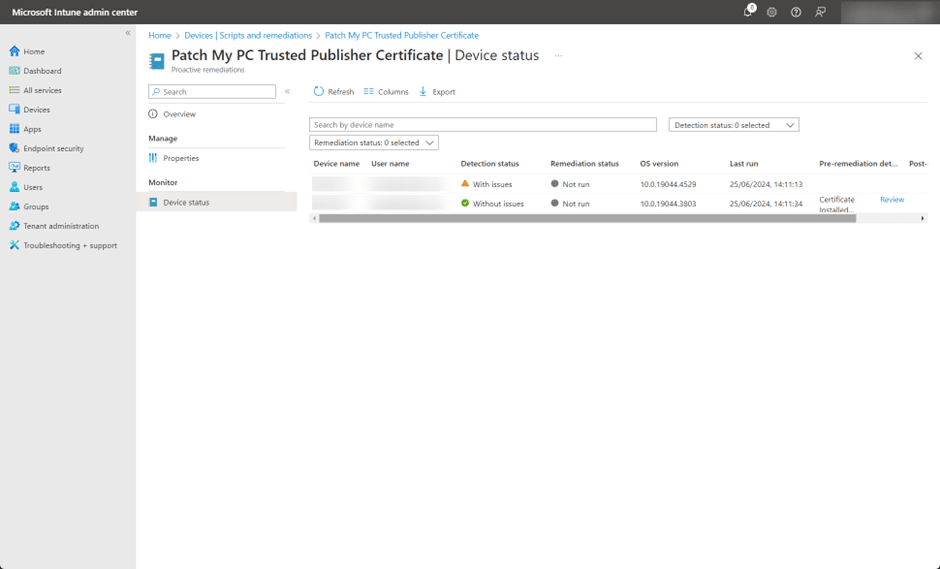
You can see the script being processed by the Intune Management Extension by looking in the HealthScriptss.log located at:
%ProgramData%MicrosoftIntuneManagementExtensionLogsObserve the Proactive Remediation Device Status blade.
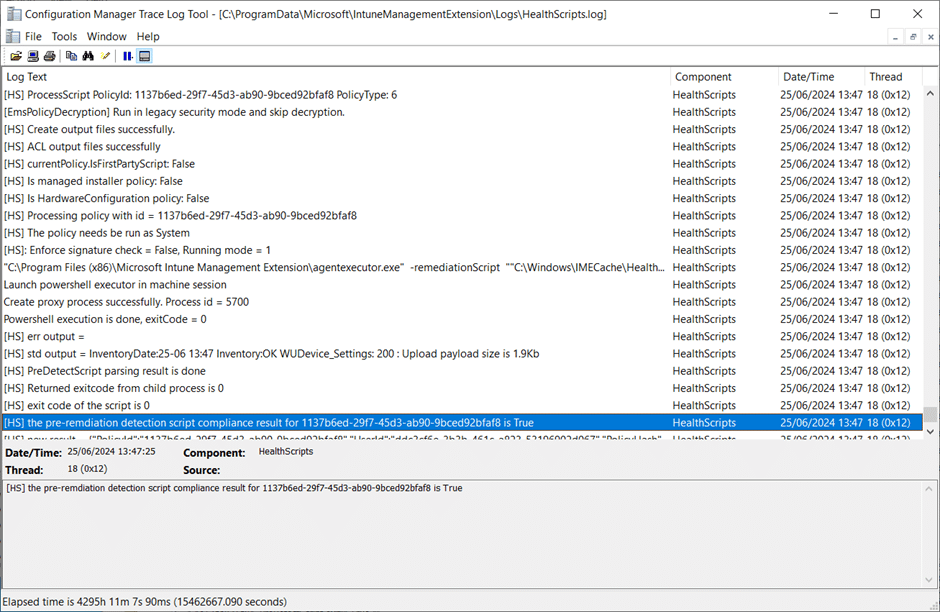
The following log snippet shows the HealthScripts.log entry if the pre-remediation (detection) script found the certificate already installed in the local computer’s Trusted Publishers store.
The following log snippet shows the HealthScripts.log entry if the pre-remediation (detection) script did not find the certificate already installed in the local machine’s Trusted Publishers store (the Exit code of the script is 1).
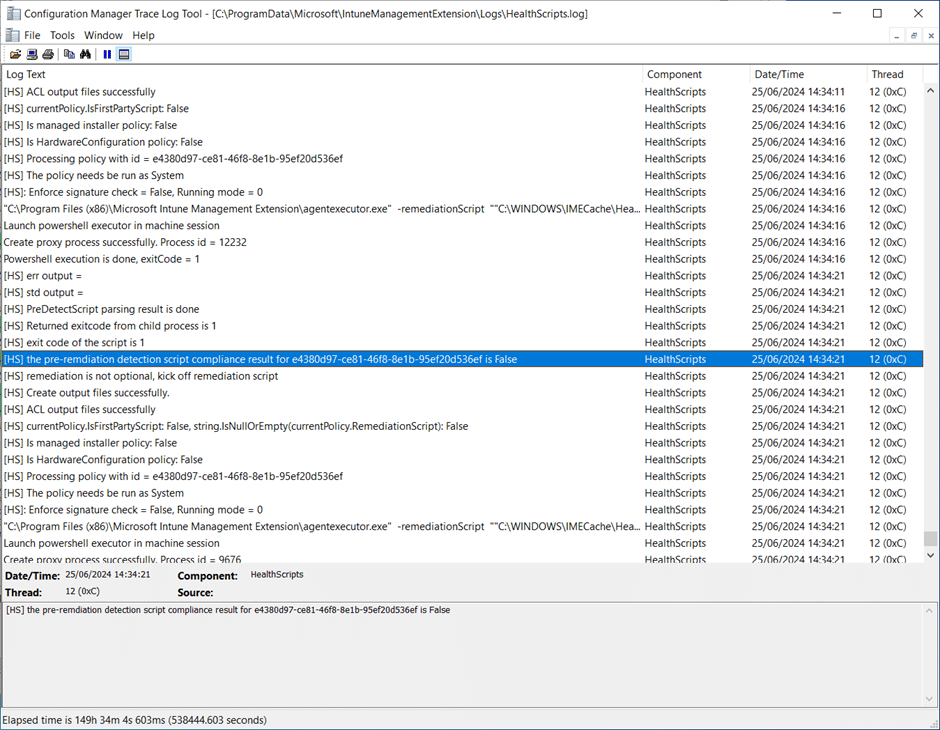
The following log snippet shows the HealthScripts.log entry if the pre-remediation (detection) script did not find the certificate already installed in the local machine’s Trusted Publishers store and the remediation script was run successfully (Exit code of the script is 0).