$500 GIFT INSIDE! We’ve all learned to recognize and avoid suspicious emails with subjects like this. Yet, while our vigilance has grown, so has the sophistication of cybercriminals. Their methods have evolved and become increasingly deceptive and difficult to detect. In light of this, staying informed and proactive in protecting ourselves against cyber attacks is crucial. Join me as we dive into the top 10 types of cyber attacks, empowering you to protect both your personal and professional endeavors from harm.
I’ve never been hacked before, so why should I care?
You’ll want to take this seriously if you care about your financial and mental well-being. The consequences of a successful cyber attack can be devastating, both personally and professionally. Cyber attackers can steal sensitive information, disrupt business operations, and cause significant financial losses. An example of this is the “WannaCry” ransomware attack that occurred in May 2017. WannaCry exploited a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows operating systems, allowing attackers to encrypt files on infected computers and demand a payment in Bitcoin to unlock the data. If this ransom was not paid, the group threatened to release the victims’ personal information. The virus spread rapidly across the globe, affecting hundreds of thousands of computers in over 150 countries, including personal computers, businesses, and even critical infrastructure like hospitals. Individuals targeted by WannaCry found their personal files encrypted and inaccessible unless they paid a fee of several hundred dollars.
With just this one example, you should be able to see that cyber attacks are a pretty big deal. Now, let’s really get into it!
Top 10 Types of Cyber Attacks
1. Phishing Attacks
A phishing attack is a type of cyber attack in which attackers try to trick individuals into providing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, and other personal data. These attacks typically involve fraudulent emails, text messages, or websites that appear to be from legitimate sources, but in reality, a cyber attacker is on the other end attempting to steal confidential information.
Look out for:
- Suspicious Sender Addresses: Phishing emails often come from addresses that look similar to, but are not exactly the same as, those of legitimate companies. For instance, an email from “support@patchmycc.com” instead of “support@patchmypc.com”.
- Generic Greetings: Be cautious of emails that start with generic salutations like “Dear Customer” instead of your actual name.
- Urgent or Threatening Language: Phishing attempts frequently create a sense of urgency or fear, warning that your account will be suspended or that you need to act immediately.
- Unexpected Attachments or Links: Don’t click on any attachments or links. Phishing links may direct you to fake websites designed to steal your information.
- Spelling and Grammar Errors: Many phishing messages contain noticeable spelling and grammatical mistakes.
Phishing is a prevalent threat, but by staying vigilant and following these guidelines, you can protect yourself from falling victim to these scams. If you’re ever unsure, contact the company to double-check the email or message is truly from them. And always remember: when in doubt, it’s better to be on the side of caution.
2. SQL Injection Attack
SQL injection is a type of cyber attack where attackers exploit vulnerabilities in a website or application’s database by manipulating the queries an application makes to its database. By injecting malicious SQL code into input fields, such as search boxes or login forms, attackers can reveal or alter sensitive information, execute administrative operations, or even delete data.
Here is an example of how this could look:
Normal Login Input
This query will check the database for the credentials inputted by a user:
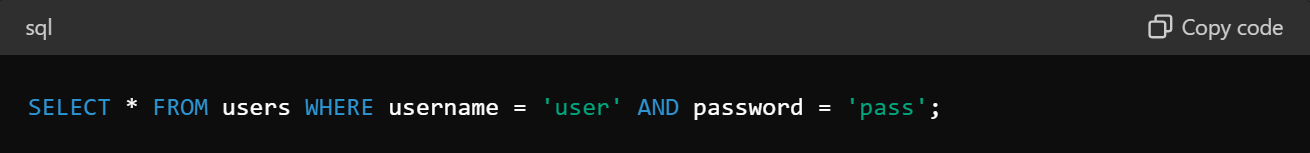
Malicious Input & Transformed Query
An attacker can modify the query to something like this:
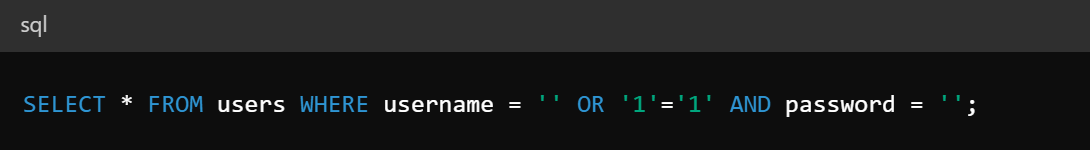
The Result of This SQL Injection
The condition OR ‘1’=’1′ is always true, causing the query to return all rows in the users table. This allows the attacker to bypass authentication without knowing any valid usernames or passwords.
Developers can better protect their applications against SQL injection attacks typically by using parameterized queries or prepared statements that safely handle user input.
If you’re looking for more information on this topic, this OSAWP guide dives deeper into how developers can prevent SQL injection attacks: SQL Injection Prevention – OWASP Cheat Sheet Series.
3. Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack
A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal functioning of a targeted server, service, or network by overwhelming it with a flood of internet traffic. The goal is to force a website, computer, or online service offline and render it unavailable to its intended users.
Different methods of executing a Denial-of-Service Attack
There are many different types of DoS attacks. Some of these include:
- Volume-Based Attacks: Floods the target with a huge amount of data to overwhelm it.
- Example: Sending too many simultaneous requests to a website.
- Protocol-Based Attacks: Exploits weaknesses in network protocols to disrupt communication.
- Example: Sending lots of connection requests to a server to make it unavailable for others.
- Application Layer Attacks: Targets specific software vulnerabilities to crash or slow down systems.
- Example: Making repeated, slow requests to a website to exhaust its resources.
- Resource Depletion Attacks: Exhaust system resources like memory or CPU power.
- Example: Sending a large, malformed packet to crash a network device.
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: Amplifies attacks by using many computers to flood the target.
- Example: Using a botnet (i.e., a network of compromised computers) to flood a website with traffic.
The Impact of a Denial-of-Service Attack
These attacks can have serious negative implications on a business and its users. Some of these include:
- Service Disruption: DoS attacks can render targeted services, websites, or networks inaccessible to legitimate users, leading to downtime and disruption of business operations.
- Loss of Revenue: Downtime from DoS attacks can directly impact revenue generation for businesses, especially those reliant on online services or e-commerce platforms.
- Damage to Reputation: Prolonged or repeated DoS attacks can erode customer trust and confidence in an organization’s ability to maintain reliable and secure services, leading to reputational damage.Understanding and implementing robust DDoS mitigation strategies is crucial for maintaining the availability and integrity of websites, servers, and networks.Here is a helpful guide by the government of Canada to help protect against a DDoS attack: Protecting your organization against denial of service attacks – ITSAP.80.100 – Canadian Centre for Cyber Security
4. Malware Attacks
A malware attack involves malicious software (AKA malware) infiltrating a computer, network, or device to cause harm, steal data, or perform unauthorized actions. Malware encompasses a wide range of malicious programs, many of which are listed in greater detail below, that each have their own unique characteristics and functionalities. These malicious programs can be spread in various ways, such as email attachments, infected websites, or software vulnerabilities.
Types of Malware
Malware is a broad term that can include various types of malicious programs, each designed for different purposes. Some known types of malware are:
- Viruses: Malware that attaches itself to legitimate programs or files and spreads to other files and systems when executed.
- Worms: Standalone malware that replicates itself to spread to other computers over a network.
- Trojans: Malicious programs disguised as legitimate software. Once activated, they can create backdoors for other malware.
- Ransomware: Malware that encrypts the victim’s data and demands a ransom for the decryption key.
- Spyware: Software that secretly monitors user activity and collects personal information without consent.
- Adware: Unwanted software designed to display advertisements, often leading to unwanted behavior and privacy concerns.
- Rootkits: Tools that allow attackers to gain undetected administrative control over a system.
- Botnets: Networks of infected devices controlled by attackers, often used to conduct large-scale attacks like DDoS.
Once installed on a system, malware can perform a multitude of malicious activities, such as stealing sensitive information, compromising system integrity, disrupting normal operations, encrypting files for ransom, and turning the infected device into a part of a botnet for further attacks.
Here are some tips by the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security to protect against malware: Protect your organization from malware (ITSAP.00.057) – Canadian Centre for Cyber Security
5. Social Engineering Hacks
Social engineering attacks are deceptive tactics used by cybercriminals to manipulate individuals into providing confidential information, gain unauthorized access to systems, or perform actions that compromise security. Unlike traditional hacking methods that rely on technical vulnerabilities, social engineers use human psychology and behavior to attack their victims.
These attacks can come in many different forms, but let’s zero in on one popular tactic. Let’s say a cybercriminal poses as a bank representative and calls a victim, pretending to offer assistance with a supposed security issue. This is how this sort of attack would play out:
- Caller Impersonation: The cybercriminal spoofs the caller ID to make it appear as if the call is coming from the victim’s bank.
- Deceptive Introduction: The cybercriminal introduces themselves as a security specialist from the victim’s bank and claims there has been suspicious activity detected on the victim’s account.
- Creating Urgency: The cybercriminal emphasizes the urgency of the situation, stating that immediate action is required to prevent unauthorized transactions or account compromise.
- Request for Information: The cybercriminal requests the victim’s personal information, such as account number, Social Security number, or login credentials.
- Threat of Consequences: The cybercriminal threatens to freeze the victim’s account if they fail to provide their information.
- Successful Data Theft: If the victim falls for the scam and provides their personal information, the cybercriminal gains access to the victim’s bank account and can now carry out fraudulent transactions or steal sensitive data.
According to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States, they receive millions of reports related to phone call scams like this each year. And this is just one of many popular examples!
6. Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is a type of cyber attack where an attacker uses a victim’s computer, smartphone, or server to mine cryptocurrency without the victim’s knowledge or consent. This can significantly slow down the affected machines, increase electricity consumption, and potentially cause hardware damage due to overheating.
One example of this happening is a true story that happened to a friend of mine! Josh discovered that his GPU was being used to mine Bitcoin. This happened through malware that had infiltrated his computer. The malware harnessed the power of Josh’s GPU to solve complex cryptographic problems, generating Bitcoin for the attacker without Josh’s consent or knowledge. Josh realized this when his GPU stats were skyrocketing, his fans were spinning like crazy, and an unknown process was consuming excessive processing power. Josh recognized this and took the necessary steps to remediate it.
This guide from the New Jersey Institute of Technology provides information on how to prevent and recover from Cryptojacking attacks: What is Cryptojacking? How to prevent, detect, and recover from it | Information Services and Technology (njit.edu).
7. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a type of security vulnerability typically found in web applications. It allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. These scripts can then be executed in the context of the user’s browser, potentially leading to unauthorized access, data theft, or other malicious activities.
How XSS Attacks Work
- Injection: The attacker identifies a vulnerable web application that does not properly sanitize user input, then they inject malicious code into the web application.
- Execution: When another user visits the compromised web page, the malicious script is executed in their browser as part of the page’s content.
- Impact: The script can perform a variety of malicious actions, such as stealing cookies or session tokens, redirecting users to malicious sites, and defacing the website.
8. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
A Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack is a type of cyber attack in which an attacker intercepts communication between two parties without their knowledge. This allows the attacker to eavesdrop, steal sensitive information, and inject malicious content into the communication stream.
Some helpful tips to prevent against a MitM attack:
- Verify SSL Certificates: Always check for valid SSL certificates when accessing websites. Be cautious of security warnings related to invalid certificates. The lock icon on a web browser indicates the site is secured with a digital certificate, meaning the data being sent between the web server and the computer is encrypted and cannot be read by others.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Transactions: Do not conduct sensitive activities, such as online banking or shopping, over public Wi-Fi networks. Instead, use a trusted network or a VPN.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all software, including operating systems and applications, up to date with the latest security patches to protect against known vulnerabilities. In my completely non-biased opinion, here is the greatest third-party patching tool to keep all your third-party apps up to date: Patch My PC: Home Page.
9. Drive-by Download
A drive-by download is a type of cyber attack where malicious software is automatically downloaded and installed on a user’s device without their knowledge or consent when they visit a compromised or malicious website. This kind of attack takes advantage of vulnerabilities in web browsers, plugins, or other software to deliver the malware without requiring any explicit action from the user, such as clicking a link or downloading a file.
A couple of examples of Drive-by-Downloads1. Angler Exploit KitThe Angler Exploit Kit was a widely used toolkit that facilitated drive-by downloads. It targeted vulnerabilities in popular software like Adobe Flash, Microsoft Silverlight, and Java. When a user visited a website compromised by Angler, the exploit kit scanned the user’s system for vulnerabilities and, if found, installed malware such as ransomware or banking trojans.2. Malvertising CampaignsAttackers often use malicious advertisements, or malvertising, to deliver drive-by downloads. For example, ads on legitimate websites like The New York Times and the BBC were found to contain malicious code. When users visited these sites, the malicious ads exploited browser vulnerabilities to install malware like CryptoLocker ransomware.
10. Password Attack
A password attack is a type of cyber attack in which an attacker attempts to gain unauthorized access to a system, account, or network by obtaining their passwords. These attacks exploit weak or compromised passwords to breach security defenses and can lead to data theft, financial loss, and other malicious activities. Password attacks come in various forms, each using different techniques to crack or steal passwords.
Here are some common methods hackers use to compromise passwords:
1. Brute Force Attack
- Description: Involves systematically trying every possible combination of characters until the correct password is found.
- Technique: Uses automated software to generate and test a large number of possible passwords.
2. Dictionary Attack
- Description: Utilizes a precompiled list of common passwords and dictionary words to guess the password.
- Technique: Automated tools run through a list of likely passwords to find matches.
3. Credential Stuffing
- Description: Involves using a list of previously breached usernames and passwords to gain access to multiple accounts.
- Technique: Hackers test stolen credentials across various websites and services using automated scripts.
To protect against password attacks, you can implement robust security practices. Use strong, unique passwords for each account to significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security, making it much harder for attackers to gain access even if they obtain your password.
Fun fact: My first ever password at the age of 7 was cookeys1.
Defend and Deter
Understanding the top 10 types of cyber attacks is crucial for ensuring robust cybersecurity defenses. From phishing to ransomware to DDoS, each attack poses unique challenges to individuals and organizations alike. You can implement some preventative measures, such as strong password policies, using firewalls and security software, and keeping software up to date.By staying informed, being proactive, and using the right tools and strategies, you and your business can better safeguard yourself against cyber threats in this increasingly interconnected world.
For further information on cybersecurity measures to mitigate any of these attacks, you can explore resources provided by organizations such as the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).CISA offers comprehensive guidance on best practices to enhance cybersecurity posture and protect against various cyber threats, enabling you to keep your most sensitive data safe and secure.